Regular Orthodontists vs. Board-Certified Orthodontists: What’s the Difference?
When seeking orthodontic treatment, you may come across the terms "orthodontist" and "board-certified orthodontist." While both professionals are qualified to straighten teeth and correct jaw alignment, there are significant differences in their training, certification, and ongoing education. Understanding these distinctions can help you make an informed decision about your orthodontic care.
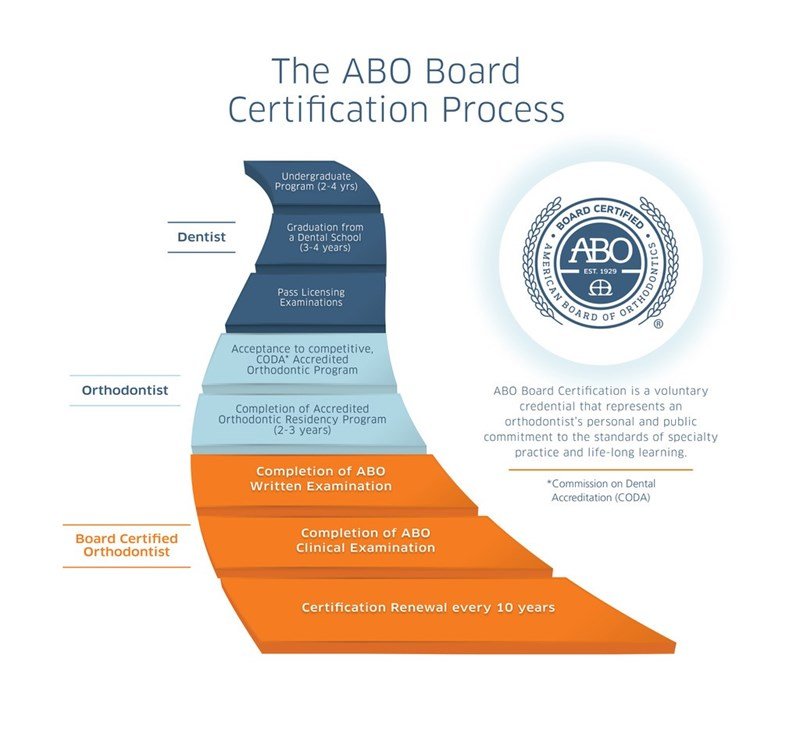
1. Education and Training
Both regular orthodontists and board-certified orthodontists must complete:
A four-year undergraduate degree
A dental degree (Doctor of Dental Surgery - DDS or Doctor of Dental Medicine - DMD)
An additional 2-3 years of specialized orthodontic residency training
This training equips them with the skills necessary to diagnose and treat misaligned teeth and jaws.
2. Board Certification: An Extra Step
A regular orthodontist can begin practicing after completing an accredited residency program. However, becoming a board-certified orthodontist requires additional rigorous testing and evaluation by the American Board of Orthodontics (ABO).
The certification process involves:
ABO Written Examination: A comprehensive test covering orthodontic principles, treatment planning, and clinical knowledge.
ABO Clinical Examination: A practical assessment where candidates present detailed case studies and demonstrate their treatment expertise.
These examinations ensure that board-certified orthodontists meet the highest standards of clinical excellence and problem-solving abilities.
3. Certification Renewal and Continuing Education
Unlike regular orthodontists, board-certified orthodontists must renew their certification every 10 years. This process involves:
Demonstrating continued proficiency in orthodontic techniques
Staying updated with the latest advancements in orthodontics
Completing continuing education courses and case evaluations
This ongoing commitment ensures that board-certified orthodontists provide the most current and effective treatments to their patients.
4. Why Board Certification Matters
Choosing a board-certified orthodontist offers several advantages:
Higher Level of Expertise: The additional certification process confirms advanced knowledge and skill.
Commitment to Excellence: Board-certified orthodontists undergo continuous education to stay ahead in their field.
Quality Assurance: The rigorous evaluation process ensures a high standard of patient care.
Conclusion
While all orthodontists are trained specialists, board-certified orthodontists take an extra step to validate their expertise through the American Board of Orthodontics. If you’re looking for an orthodontist committed to the highest level of patient care, choosing a board-certified professional can provide added confidence in your treatment outcome. Whether you choose a regular orthodontist or a board-certified one, ensuring they meet your needs and treatment goals is essential for achieving a healthy, beautiful smile.